XYPlot
The XYPlot panel is available in Product Explorer tabs. Users can create, export and import XY data and graphs. XYPlot can be accessed through the Edit option in the context menu, or through the shortcut in the toolbar.
XYPlot Types
IDs Path
Transient
Min Max
Force Deflection
Harmonic
XYPlots are classified into Editable and Non-Editable. Imported and Merged Plots are always non-editable.
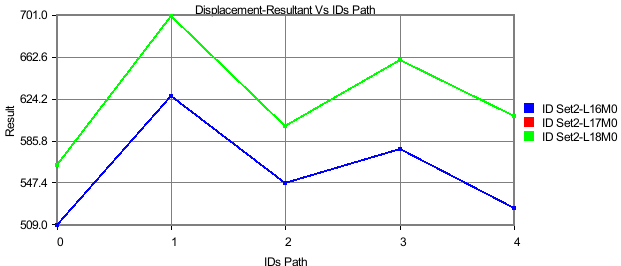
IDs Path Plot
In this plot,
X axis : IDs Path or CAE Result
Y axis: CAE Result
Inputs : ID sets, Instances. A Node ID set or path is a sequential list of IDs.
Users can define multiple paths or ID sets. One curve corresponds to one ID set per instance.
They can fix the instance and vary the ID path to understand how each path varies against the sequence. Similarly, users can keep the ID path fixed and vary the selection of instances to understand how the sequential path varies between instances on time steps. Users also have the option to vary both ID path and selection of instances.
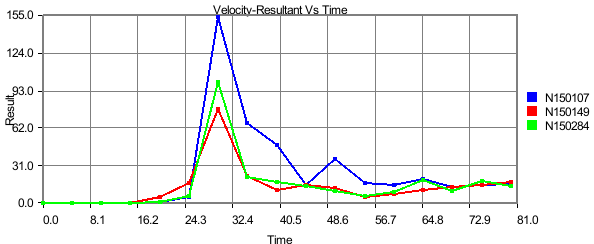
Transient Plot
In this plot,
X axis: Time/Frequency/Instance Number/ CAE Result.
Y axis: CAE Result.
Input: Node ID sets. Instances.
Each curve refers to a nodal ID and how its CAE result varies over time or frequency or instances.
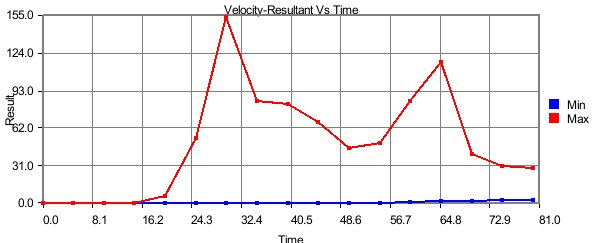
Min Max Plot
In this plot,
X axis: Time/Frequency/Instance Number/ CAE Result.
Y axis: CAE Result.
Input: Instances.
Min curve refers to the minimum of CAE results over the instances.
Max curve refers to the maximum of CAE results over the instances.
So the min/max curves will vary according to visible parts.
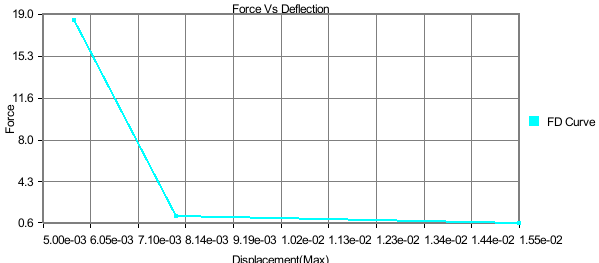
Force Deflection Plot
In this plot,
X axis: Maximum of displacement result.
Y axis: Sum of reaction forces.
Input: Node ID sets, Instances.
A force deflection plot represents one Node ID set, sum of forces of Node ID set list and how it varies over the maximum displacement of Node ID set over instances. This type of plot will be listed only if the CAE model contains Displacement and Reaction Force results.
This is a special case of transient plot. A set of IDs are considered as input to this plot. For each instance or time step, Reaction Force / Force Loads and Displacement values of these IDs are considered. The maximum displacement values for all instances provide the range for the X axis. Sum of Reaction Force values is considered for the Y axis. This plot contains a single curve.
For example, let the number of instances be 4. Let the ID’s selected be { ID1, ID2, ID3}. The following table provides Reaction Force and Displacement values of these IDs over the instances.
ID1
ID2
ID3
Sum(ID1+ID2+ID3)
ID1
ID2
ID3
Max(ID1,ID2,ID3)
T1
U11
U12
U13
F1
V11
V12
V13
D1
T2
U21
U22
U23
F2
V21
V22
V23
D2
T3
U31
U32
U33
F3
V31
V32
V33
D3
T4
U41
U42
U43
F4
V41
V42
V43
D4
X Axis Range = Min/Max (D1,D2,D3,D4);
Y Axis Range = Min/Max (F1,F2,F3,F4);
In other words, the data points of the curve are as follows,
{ (D1,F1), (D2,F2), (D3,F3), (D4,F4) }.
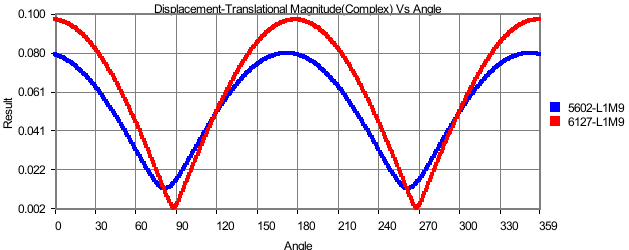
Harmonic Plot
In this plot,
X axis: Angle (0 to 360)
Y axis: Complex Derived Result
Input: Node ID sets, Instances.
This plot is applicable only for complex Eigen results. Harmonic plot displays the variation of any complex results with respect to angle (= ωt). Using this plot, users can identify the angle for which a derived result is maximum.
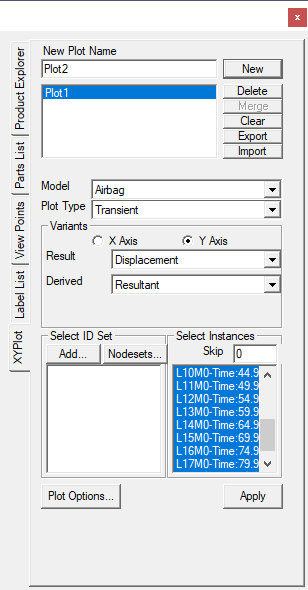
XYPlot Panel
The various controls and fields available in the XYPlot panel are:
Plot Name
Enter plot name
New
Creates an empty XYPlot template. The newly created plot will appear in the list box
Delete
Deletes the selected plots
Merge
Merges selected plots into a new XYPlot
Clear
Clears current graph data
Export
Exports the graph table data into a comma separated file. (csv)
Import
Imports the comma separated file in the specified format
Model
Allows the user to select a CAE model
Plot Type
Possible plot types for the selected CAE model will be listed. Users can select one of them
Variants
Defines the X and Y axis variants.
Result
Users can select a possible result for X/Y axis
Derived
Users can select a derived scalar type
Complex
Users can select complex components of results and enter angle in degrees. This option is applicable and enabled for complex eigen data result
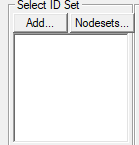
Add
Opens up a Node ID set dialog to define Node ID sets. Defined Node ID set names are appended to the XYPlot panel as well in the opened panel.
Nodesets
Allows user to select nodesets from CAE Nodeset Manager from a pop up dialog. User can select only if nodesets are available
Select ID set
Users can select multiple Node ID sets
Select Instances
Users can select multiple instance names.
Skip
Users can filter and select instances by skipping a specified number in case of huge instance list.
Steps to create an XYPlot
Open XYPlot from the left span or click Edit | XYPlot
Enter the XYPlot name in the text box.
Click New.
Make sure that an empty XYPlot is displayed in the viewer and plot name is appended in the list box.
Select a CAE model from the Model drop down list.
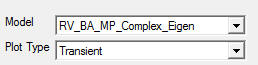
Select the plot type you wish to build.
Select the variants for X and Y axes. An X variant may be a CAE result or result attribute.
Y variant should be of CAE result.
If the result is complex, please select complex component Real, Imaginary, Magnitude,
Phase and Angle.
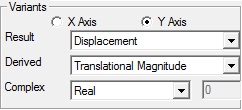
Select the appropriate derived scalar for both axes.
Click Add to define the ID sets.
It opens up the ID Set dialog box.
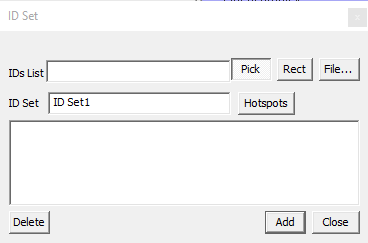
Users have the following options to provide Node ID set.
Enter the known Node IDs in the text box separated by commas,
Pick the Node IDs in the viewer,
Provide a file which contains Node IDs
Use Rect for window selection on the model
Get CAE probed or hotspot labels.
To pick the Node ID from the viewer, enable the Pick push button.
Click Nodes in the viewer. Node ID points are highlighted with red color. Node IDs are appended to the text box in the dialog for each click.
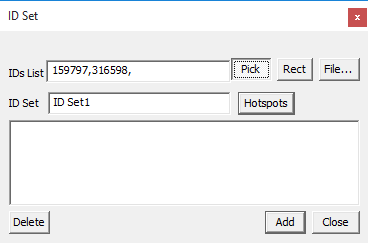
All points are connected by a line to show the sequence or path.
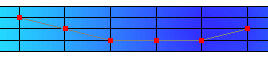
To select by window, click Rect which enables mouse mode for window selection. Click and drag to define the window on the model using the left mouse button.
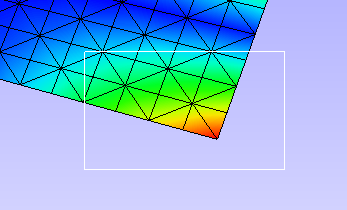
All node IDs within the window are highlighted as red spots.
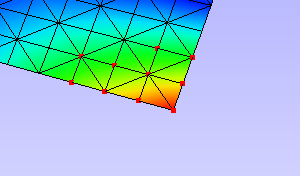
Click Hotspots to bring all IDs for probed or hotspot labels that exist
Enter an ID set name.
Click Add to create the ID set
The newly created ID set is listed in the XYPlot panel.
Select the ID sets required for your plot. ID set selection is not required for Min Max XYPlot.
Select the Instances required for the plot. If the instance list is too large for selection, users can filter using the Skip option.
Skip option skips every nth instance between every consecutive selection. Where n is the number entered by the user in the Skip text.
Click Apply to construct the XY Plot with the above information and display it in the viewer.
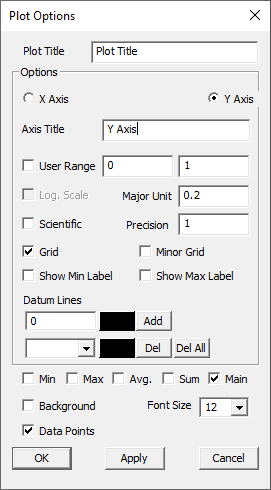
Plot Options Panel
The Plot Options button found in the XYPlot panel opens up the below panel
The fields and controls available in the Plot Options panel is explained below
Plot Title |
Displays plot title which can be edited |
Axes Title |
Displays axes title which can be edited |
User Range |
Allows user to enter min and max value |
Log Scale |
Toggles between Logarithmic and Decimal Scale for the selected axis. |
Major Unit |
Major unit for axis tick mark |
Scientific |
Toggles between Scientific and Decimal format |
Precision |
Allows users to change the precision value in the format. |
Grid |
Displays axis grid |
Show Min Label |
Displays the minimum result data point in a label |
Show Max Label |
Displays the maximum result data point in a label |
Datum Lines |
Allows users to enter a value within the axis range to render a datum or reference line. A color can be defined for each datum line. |
Add |
User defined datum value and color is validated and added to the list. |
Del |
Deletes the datum line selected in the list. |
Del All |
Deletes all datum lines. |
Min |
Shows/Hides a curve with minimum of all y axis values against x axis invariant values. |
Max |
Shows/Hides a curve with maximum of all y axis values against x axis invariant values. |
Sum |
Displays a curve with sums of all y axis values against x axis invariant values. |
Avg |
Shows/Hides a curve with an average of all y axis values against x axis invariant values. |
Main |
Shows/Hides the actual curves |
Background |
Allows users to select background color and set it. |
Font Size |
Allows users to change font size. |
Data Points |
Show/ Hide data points |
Steps to modify the XYPlot style
Create a plot and construct with CAE data
XYPlot can be modified with text formats
Click Plot Options in the XYPlot panel Or Use “Ctrl + Double Click” to open up XYPlot Options dialog box.
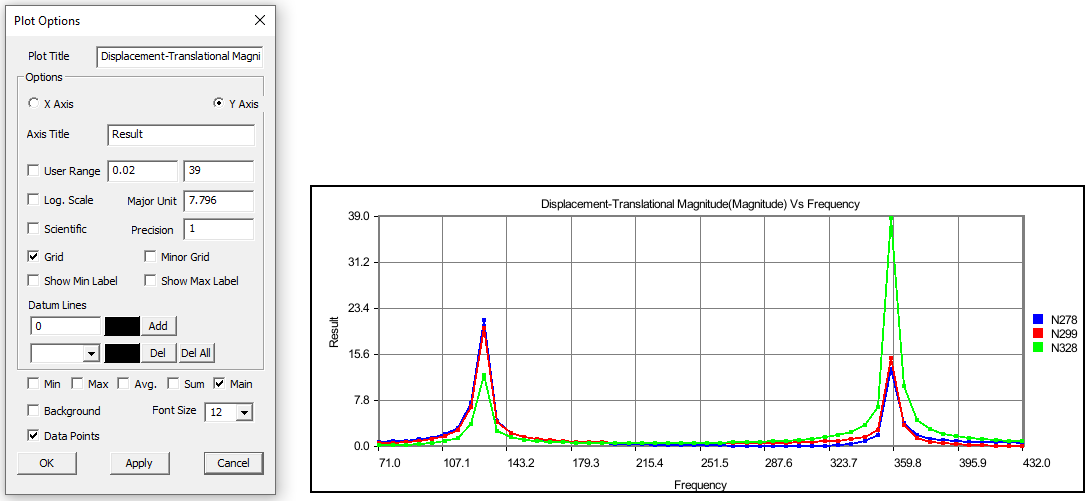
Change the plot titles.
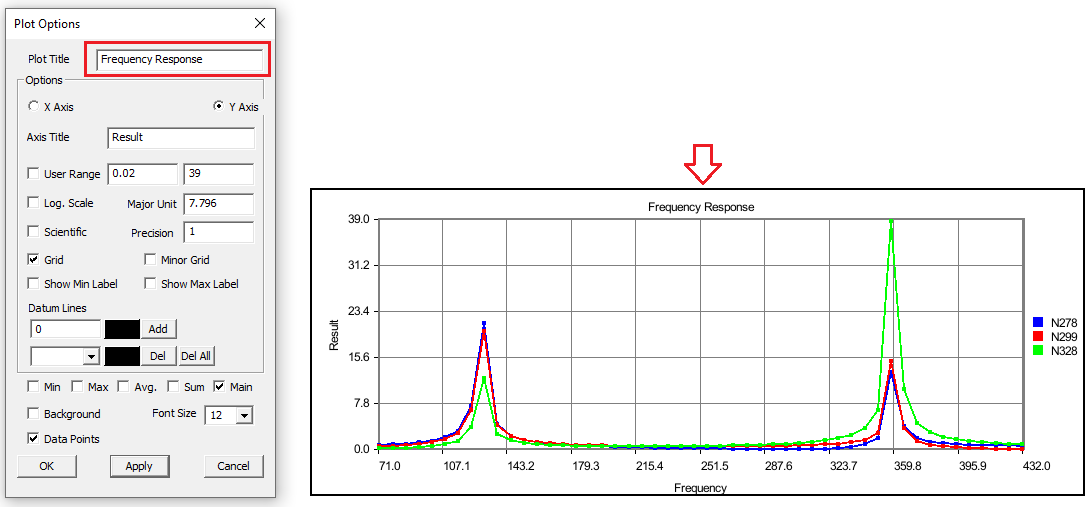
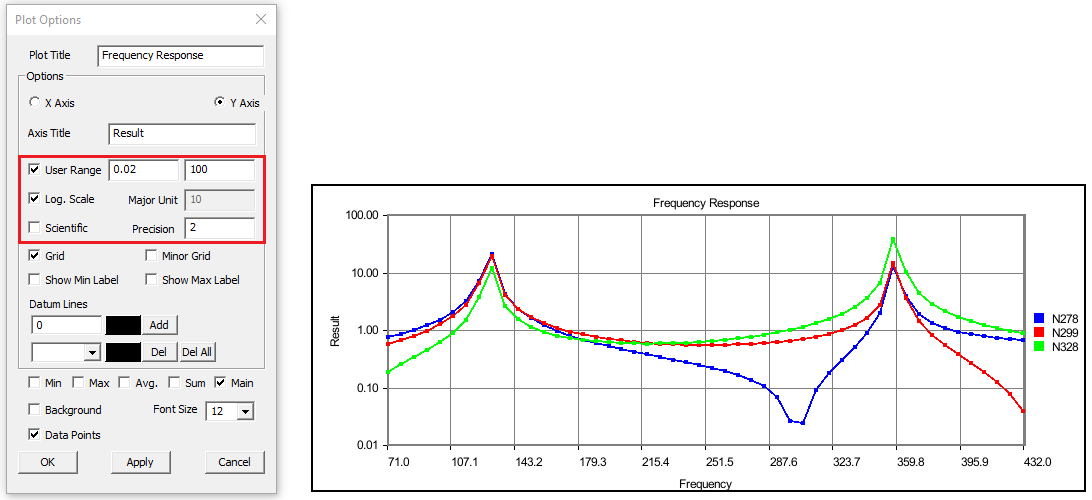
Change Y axis user range, major unit and precision values.
Change X Axis range, major unit and precision values.
Grids for each axis can be switched on/off.
Click Sum, Max, Min and Average options and uncheck main.
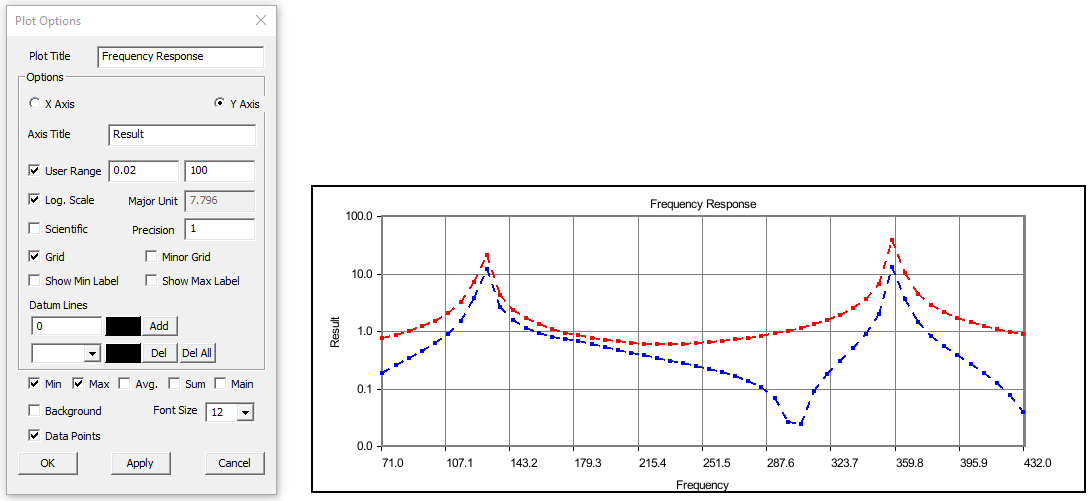
All these special curves can be seen in stippled lines. Sum curve will be seen in dark brown, Max curve in Red, Min Curve in blue and Average curve in magenta.
If there is a large variation between curves then log. scale can be used for corresponding axis.
Scientific format can be used when tick mark texts are lengthy.
Enable Background to set background color.
Steps to add datum lines
Select either X or Y axis.
Enter a value, which is within the range.
Select a color corresponding to datum value from the color window.
Click Add.
Datum line and color will be added and rendered imJPGImagestely and is added to datum list combo box
Repeat the steps to add more datum lines.
Select a datum line to be deleted by its value and click Del
Click Del All to delete all datum lines for the axis.
Datum lines are drawn in stipple lines by default.
VCollab stores all datum lines into viewpoint and CAX. Below is a sample plot with datum lines for each axis.
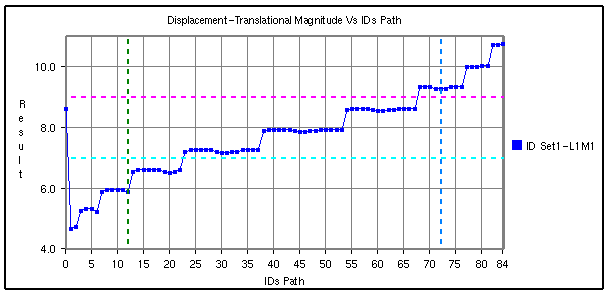
Steps to select, move and resize the plot
Click a plot name in the plot list of XYPlot panel Or Double click the plot in the viewer
The XYPlot will be highlighted and ready for moving resizing.
Move mouse cursor over plot. Mouse cursor will change to
 .
Drag the mouse to move the plot.
.
Drag the mouse to move the plot.Move the mouse to the plot edges and notice that mouse cursor symbol is changing to
 Click and drag the mouse with the resize
symbol to resize the plot.
Click and drag the mouse with the resize
symbol to resize the plot.Double click to select plot regions.
Selected region can be resized.
Steps to merge plots
Select XYPlots in the plot list panel.
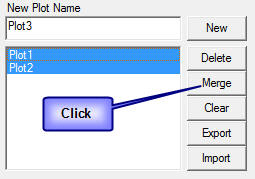
Click Merge.
A new Non-Editable plot is created and appended in the list. All dialog controls will be disabled for the non-editable merged plot.
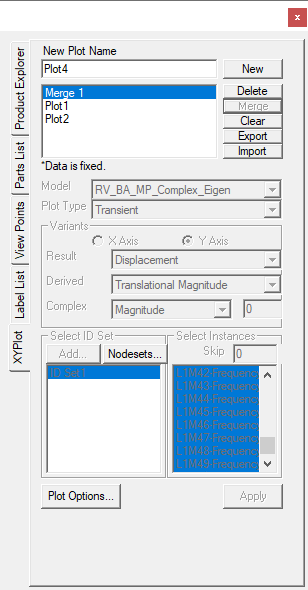
The same plot is displayed and highlighted in the viewer.
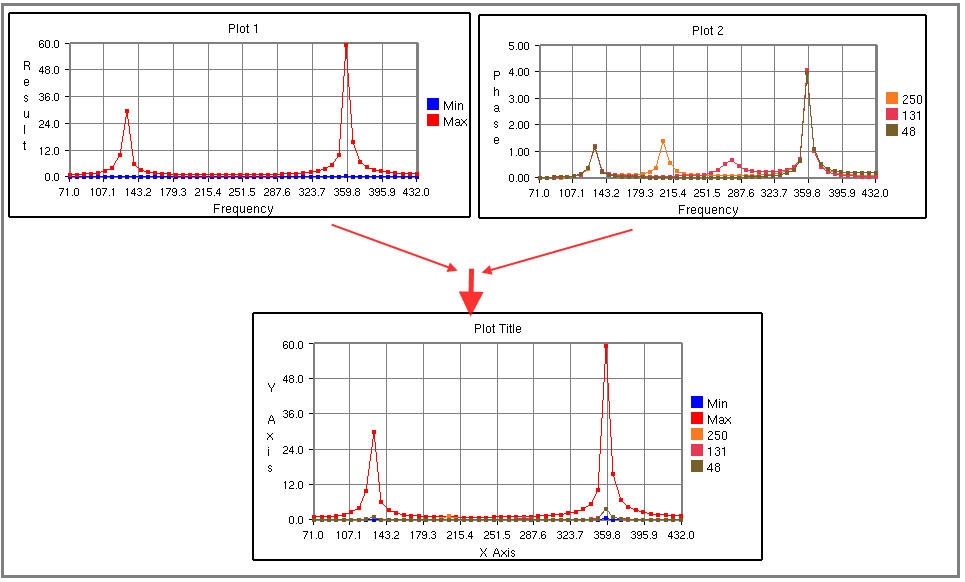
Steps to export and import XYPlot data
Select XYPlots from the plot list.
Click Export which opens up file-save dialog.
Enter a filename.
Plot name is suffixed to the file name. Each plot is exported as one csv file.
To load existing plot files,
Click Import which opens the file browser dialog with file type .csv by default. VCollab supports csv files and LSDyna binout data files.
The CSV file should be in a particular format as explained later in this module.
Select all the XYPlot CSV files and click open.
All plots are imported as Non-Editable plots as it does not contain CAE information.
Change the File type in the file browser dialog as binout to import LSDyna binout data.
Note
If the binout file’s name or extension does not include the keyword ‘binout,’ it will be excluded due to the filter. In this case, the user should set the file type to ‘All files (*.*)’ and manually select the relevant file.
Steps to edit XYPlot curve color
Select the XYPlot.
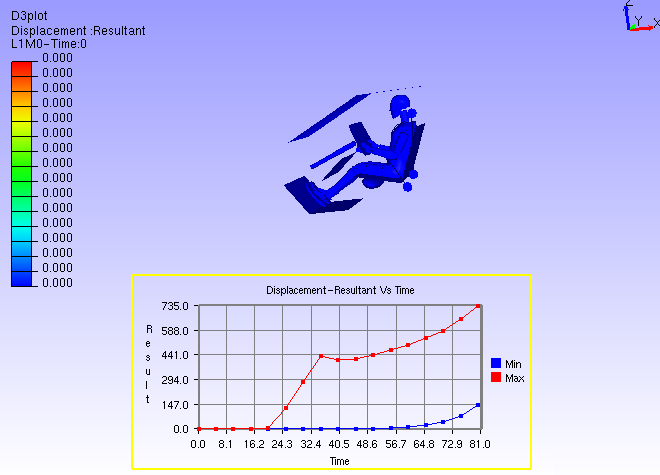
Double click on the Plot Legend rectangle to highlight it.
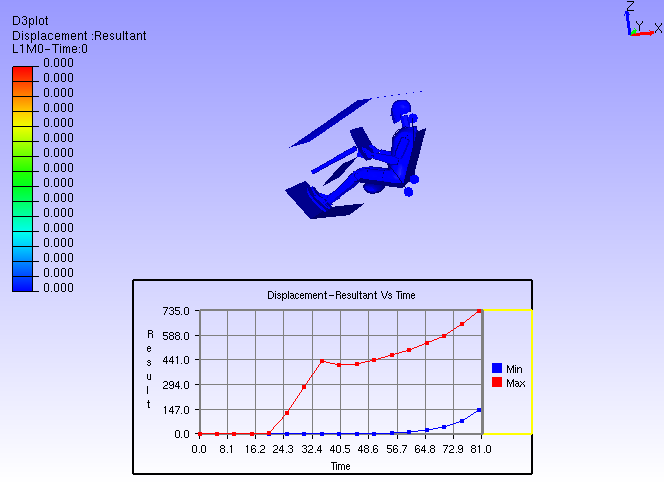
Click on the color palette box to open Curve Edit dialog.
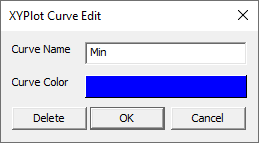
Edit the curve name if required.
Click the color window to edit curve color.
XYPlot Data File Format
This is a comma separated value (CSV) file and can be viewed in spread sheets.
Format 1 - VCOLLAB_XYPLOT_FILE_CSV_X_SINGLE
In this format, x axis values are same for all curves. First column refers to X axis and other columns refers to curve Y axis values.
Line 1
File Type Header
VCOLLAB_XYPLOT_FILE_CSV_X_SINGLE
Line 2
Titles (Optional)
#Titles,<plot_title>,<x-axis_tile>, <y-axis_title>
Line 3
Column Headers
<X axis Invariant>,<Curve1 Name>,<Curve 2 Name>, …,
Line 4
Value 1
<val>,<val>,<val>,…,
Line 5
Value 2
<val>,<val>,<val>,…,
Line …
Value ..
<val>,<val>,<val>,…,
Line N
Value N
<val>,<val>,<val>,…,
<EOF>
Example :
VCOLLAB_XYPLOT_FILE_CSV_X_SINGLE
Time,Node1, Node2, Node3,
0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 0.023,
0.1, 2.0, 0.35,1.023,
0.25,3.0,0.023,2.653,
0.302, 4.0,0.02,2.023,
0.43,13.0,0.5,1.023,
0.5,17.0,1.5, 2.023,
Format 2 - VCOLLAB_XYPLOT_FILE_CSV_X_SINGLE_ATTRIBUTE
Here one more column is introdouced to track the data points based on its attribute values. This will be useful to compare two different curve positions for a given attribute. Attribute can be time, frequency, angle, etc.
Line 1
File Type Header
VCOLLAB_XYPLOT_FILE_CSV_X_SINGLE_ATTRIBUTE
Line 2
Titles (Optional)
#Titles,<plot_title>,<x-axis_tile>, <y-axis_title>
Line 3
Column Headers
<Attribute_Name>, <X axis Invariant>, <Curve1 Name>,<Curve 2 Name>, …,
Line 4
Value 1
<attrib_val>,<val>,<val>,<val>,…,
Line 5
Value 2
<attrib_val>,<val>,<val>,<val>,…,
Line …
Value ..
<attrib_val>,<val>,<val>,<val>,…,
Line N
Value N
<attrib_val>,<val>,<val>,<val>,…,
<EOF>
Example :
Format 3 - VCOLLAB_XYPLOT_FILE_CSV_X_MULTIPLE
This format contains multiple curves without any constant X axis invariant. As there is no common relation curve datapoints, each curve is written one after the other in two columns.
Line 1
File Type Header
VCOLLAB_XYPLOT_FILE_CSV_X_MULTIPLE
Line 2
Titles (Optional)
#Titles,<plot_title>,<x-axis_tile>, <y-axis_title>
Line 3
Column Headers
<X Axis_Name>, <Y Axis Name>
Line 4
Curve1 Name
[Curve Name: curve1]
Line 5
Value 1
<val>,<val>,
Line 6
Value 2
<val>,<val>,
Line …
Value ..
<val>,<val>,
Line k
Value k
<val>,<val>,
Line k+1
Empty Space
Curve1 Name
[Curve Name: curve 2]
Value 1
<val>,<val>,
Value 2
<val>,<val>,
…
Value ..
<val>,<val>,
Line N
Value N
<val>,<val>,
<EOF>
Example:
Format 4 - VCOLLAB_XYPLOT_FILE_CSV_X_MULTIPLE_ATTRIBUTE
This format contains multiple curves without any constant X axis invariant. As there is no common relation curve datapoints, each curve is written one after the other in two columns.
Line 1
File Type Header
VCOLLAB_XYPLOT_FILE_CSV_X_MULTIPLE_ATTRIBUTE
Line 2
Titles (Optional)
#Titles,<plot_title>,<x-axis_tile>, <y-axis_title>
Line 3
Column Headers
<Attribute Name>, <X Axis_Name>, <Y Axis Name>
Line 4
Curve1 Name
[Curve Name: curve1]
Line 5
Value 1
<atrib_val>,<val>,<val>,
Line 6
Value 2
<atrib_val>,<val>,<val>,
Line …
Value ..
<atrib_val>,<val>,<val>,
Line k
Value k
<atrib_val>,<val>,<val>,
Line k+1
Empty Space
Curve2 Name
[Curve Name: curve 2]
Value 1
<atrib_val>,<val>,<val>,
Value 2
<atrib_val>,<val>,<val>,
…
Value ..
<atrib_val>,<val>,<val>,
Line N
Value N
<atrib_val>,<val>,<val>,
<EOF>
Note
Line 2 in all formats, is optional. User can use this format without line number 2.
Example:
VCOLLAB_XYPLOT_FILE_CSV_X_MULTIPLE_ATTRIBUTE
Time,Velocity,Result
[Curve Name:N201]
0,0,0,
4.99443,5.97401e-06,0,
9.99323,2.80677e-05,0.000371262,
14.9916,0.00137967,0.00325967,
19.993,0.00841877,0.0122644,
24.9934,0.0215457,0.0405959,
29.9992,0.0280345,0.172643,
34.9985,0.043332,0.49279,
[Curve Name:N234]
0,0,0,
9.99323,0.324686,0.787124,
19.993,6.10108,9.28285,
29.9992,154.139,283.757,
34.9985,84.6285,436.429,
|
Binout Plot
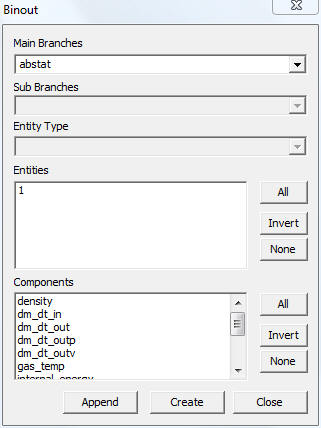
The controls and fields available in the Binout plot panel and explained below.
Main Branches |
Lists main branches in binout data |
Sub Branches |
Lists sub branches or sub directories |
Entity type |
This option is enabled if there is a classification among entities |
Entities |
Lists all entities available for selected main branch, sub branch and entity type. |
Components |
Lists all result components available to the entities |
All |
Selects all entities or components |
Invert |
Inverts the selection of entities or components |
None |
Deselects all selection |
Append |
Appends data into current XYPlot |
Create |
Clears current XYPlot data and appends binout data. |
Steps to Import LSDyna binout data into VCollab XYPlot
Click Import to open up file browser dialog.
Select LSDyna Binout files (binout) in the file type drop down in the file browser dialog.
Note
If the binout file’s name or extension does not include the keyword ‘binout,’ it will be excluded due to the filter. In this case, the user should set the file type to ‘All files (*.*)’ and manually select the relevant file.
Select a binout file, which will be validated against binout format. It gives an error if file format validation fails.
A new user interface for Binout opens up.
Select a main branch, which changes all other lists.
Select a sub branch which changes list under sub branch.
Entity type will be enabled only if there is a group classification based on result component or entity levels (master, slave, etc). Select an entity type if it is enabled.
Select multiple entities holding the Ctrl key
Similarly, select multiple components.
Click Create to create a new plot with these data.
Error messages will be shown for missing minimum selection data.
Click Append to append the data to current XYPlot.
History Data
History files can be generated from VMoveCAE. History data is written in *.json format which can be imported into VCollab Pro XYPlot module. XYPlot opens up the history data interface when a JSON file is imported.
History Plot Panel
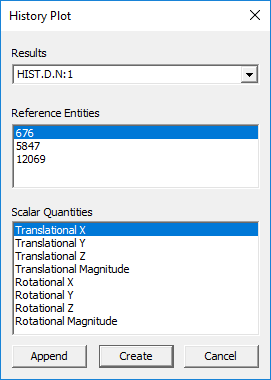
The controls and fields available in XYPlot panel are explained below
Results |
Lists history results. |
Reference Entities |
This may be Global or Node IDs or Element IDs. |
Scalar Quantities |
Lists possible scalar results that can be derived, for current selected result. |
Create |
Creates a new XYPlot for the selected attributes. |
Cancel |
Closes dialog. |
Steps to import history plot (.json) files
Open XYPlot panel
Click Import to open up the file browser dialog box.
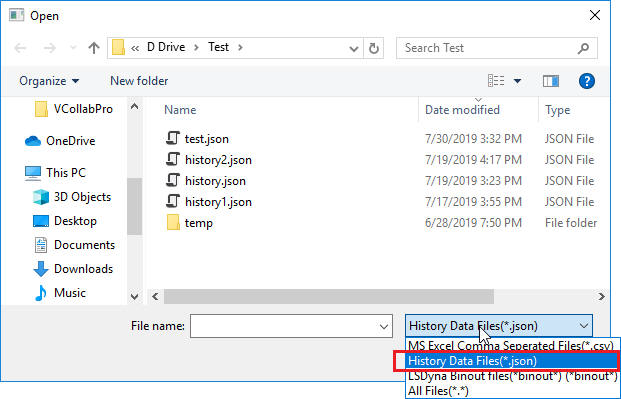
Select file type as History data files (*.json)
Select the desired history data file and click Open.
The History Plot panel opens.
Select a result from the dropdown list.
Select reference entities if available.
Select the scalar components if available
Click Append to append the history curve into the existing plot.
Click Create to create a new XYPlot and append the selected curves.
History file format (JSON)
{
“Tables”: [
{
“Name”: “Step-1”,
“X Axis”: {
“Name”: “Frequency”,
“Values”: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16]
},
“Results”: [
{
“Name”: “Unknown - Vibration mode”,
“Result Type”: “Scalar”,
“References”: [
{
“ID”: “”,
“Type”: “Global”,
“Components”: [
{
“Component Type”: “”,
“Values”: [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
}
]
}
]
},
{
“Name”: “Unknown - Vibration mode”,
“Result Type”: “Scalar”,
“References”: [
{
“ID”: “”,
“Type”: “Global”,
“Components”: [
{
“Component Type”: “”,
“Values”: [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
}
]
}
]
},
{
“Name”: “Unknown - Vibration mode”,
“Result Type”: “Scalar”,
“References”: [
{
“ID”: “”,
“Type”: “Global”,
“Components”: [
{
“Component Type”: “”,
“Values”: [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
}
]
}
]
},
{
“Name”: “Unknown - Vibration mode”,
“Result Type”: “Scalar”,
“References”: [
{
“ID”: “”,
“Type”: “Global”,
“Components”: [
{
“Component Type”: “”,
“Values”: [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
}
]
}
]
},
{
“Name”: “Unknown - Vibration mode”,
“Result Type”: “Scalar”,
“References”: [
{
“ID”: “”,
“Type”: “Global”,
“Components”: [
{
“Component Type”: “”,
“Values”: [ 0.188, 0.000, 0.003, 0.022, 0.270, 0.000, 0.067, 0.001 0.006, 0.009, 0.000, 0.002, 0.057, 0.012, 0.003, 0.008 ]
}
]
}
]
},
{
“Name”: “Unknown - Vibration mode”,
“Result Type”: “Scalar”,
“References”: [
{
“ID”: “”,
“Type”: “Global”,
“Components”: [
{
“Component Type”: “”,
“Values”: [ 4.12, 0.03 0.02, 0.66, 0.16, 0.09, 0.06, 0.04, 0.00, 0.02, 0.01, 0.00, 0.00, 0.0, 0.00, 0.00 ]
}
]
}
]
},
{
“Name”: “Unknown - Vibration mode”,
“Result Type”: “Scalar”,
“References”: [
{
“ID”: “”,
“Type”: “Global”,
“Components”: [
{
“Component Type”: “”,
“Values”: [ 13.35, 1.27, 0.01, 2.02, 0.54, 0.00, 0.24, 0.03, 0.02, 0.46, 0.29, 0.00, 0.05, 0.00, 0.00, 0.01 ]
}
]
}
]
},
{
“Name”: “Unknown - Vibration mode”,
“Result Type”: “Scalar”,
“References”: [
{
“ID”: “”,
“Type”: “Global”,
“Components”: [
{
“Component Type”: “”,
“Values”: [ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 ]
}
]
}
]
},
{
“Name”: “Unknown - Vibration mode”,
“Result Type”: “Scalar”,
“References”: [
{
“ID”: “”,
“Type”: “Global”,
“Components”: [
{
“Component Type”: “”,
“Values”: [ 55.07, 12.9, 15.8, 16.1, 16.8, 22.8, 29.6, 35.4, 48.6, 55.2, 58.9, 61.5, 74.8, 87.4, 81.2, 90.2 ]
}
]
}
]
},
{
“Name”: “Unknown - Vibration mode”,
“Result Type”: “Scalar”,
“References”: [
{
“ID”: “”,
“Type”: “Global”,
“Components”: [
{
“Component Type”: “”,
“Values”: [ 1e-8, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 ]
}
]
}
]
},
{
“Name”: “Unknown - Vibration mode”,
“Result Type”: “Scalar”,
“References”: [
{
“ID”: “”,
“Type”: “Global”,
“Components”: [
{
“Component Type”: “”,
“Values”: [ 8e-8, -3e-8, 0, -6e-8, -2e-8, 1e-8, -2e-8, 0, -1e-8, 2e-8, 0, 1e-8, -1e-8, 0, 0, 0 ]
}
]
}
]
},
{
“Name”: “Unknown - Vibration mode”,
“Result Type”: “Scalar”,
“References”: [
{
“ID”: “”,
“Type”: “Global”,
“Components”: [
{
“Component Type”: “”,
“Values”: [ 1.3e-7, 0, 0, -8e-8, -2e-8, 0, 0, 1e-8, 2e-8, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 ]
}
]
}
]
},
{
“Name”: “Unknown - Vibration mode”,
“Result Type”: “Scalar”,
“References”: [
{
“ID”: “”,
“Type”: “Global”,
“Components”: [
{
“Component Type”: “”,
“Values”: [ -0.4, 0.01, 0.05, -0.1, 0.52, 0.02, 0.25, -0.0, 0.07, -0.0, -0.0, -0.0, -0.2, -0.1, -0.0, 0.09 ]
}
]
}
]
},
{
“Name”: “Unknown - Vibration mode”,
“Result Type”: “Scalar”,
“References”: [
{
“ID”: “”,
“Type”: “Global”,
“Components”: [
{
“Component Type”: “”,
“Values”: [ 2.04, 0.28, -0.1, 0.82, 0.42, -0.1, 0.26, -0.1, 0.08, -0.0, -0.2, -0.0, 0.00, -0.0, 0.02, -0.0 ]
}
]
}
]
},
{
“Name”: “Unknown - Vibration mode”,
“Result Type”: “Scalar”,
“References”: [
{
“ID”: “”,
“Type”: “Global”,
“Components”: [
{
“Component Type”: “”,
“Values”: [ 3.65, 1.12, 0.12, 1.42, 0.74, 0.08, 0.49, -0.1, 0.15, -0.6, -0.5, -0.0, 0.23, 0.00, -0.0, 0.03 ]
}
]
}
]
},
{
“Name”: “Unknown - Vibration mode”,
“Result Type”: “Scalar”,
“References”: [
{
“ID”: “”,
“Type”: “Global”,
“Components”: [
{
“Component Type”: “”,
“Values”: [ 11.8, 17.7, 20.0, 20.3, 20.3, 23.8, 27.3, 30.0, 34.0, 37.8, 38.2, 39.4, 43.2, 46.0, 47.2, 47.9 ]
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
|